Internet exchange made simple.
FD-IX is a modern solution to peering and connectivity. We provide interconnection in 31 datacenters across the United States.
SOLUTIONS & NETWORK PARTNERSHIPS
Our strategic alliances with industry leaders; delivering enhanced connectivity, performance, and global reach for our members.
LATEST NEWS & UPDATES
Stay informed about our network developments and industry insights.

National Broadband Co-Op (AS400701) Joins FD-IX, Strengthening Regional Connectivity
The National Broadband Co-Op (NBBC) has taken a major step in its mission to support independent Internet providers by joining Fiber Data Internet Exchange (FD-IX). NBBC, operating under AS400701, represents operators serving small towns, rural communities, and regions where the Internet relies on collaboration as much as fiber. FD-IX exists for that same reason. It brings networks together so traffic can move across the Midwest without detours through far-off cities. When updates, video stream
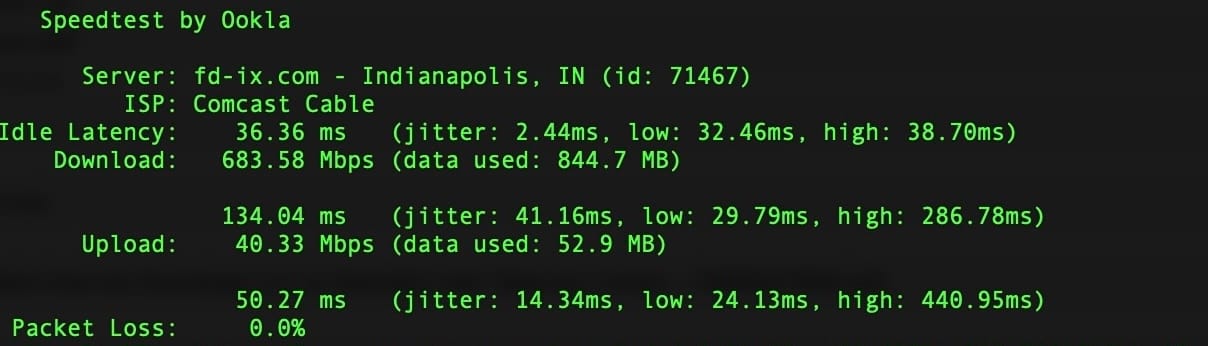
How to Run a Speed Test with Ookla’s CLI on the FD-IX Public Server
If you want a fast and straightforward way to test performance to FD-IX, Ookla’s Speedtest CLI is a simple tool you can use anywhere you have terminal access. FD-IX has a public Ookla test server that lets ISPs, MSPs, and engineers measure actual throughput and latency across the exchange. You can use it to check your routing, look for congestion, and make sure your path into the IX is local. You can run the test from Linux, macOS, Windows PowerShell, routers with shell access, or even small la

MSPs can benefit from FD-IX
Joining an Internet Exchange like FD-IX can give MSPs a real advantage, even if it’s not always obvious.
Ready to exchange traffic?
Join dozens of networks and reduce your transit costs today.